an atmospheric chemistry Lab at the University of virginia
read our recent work


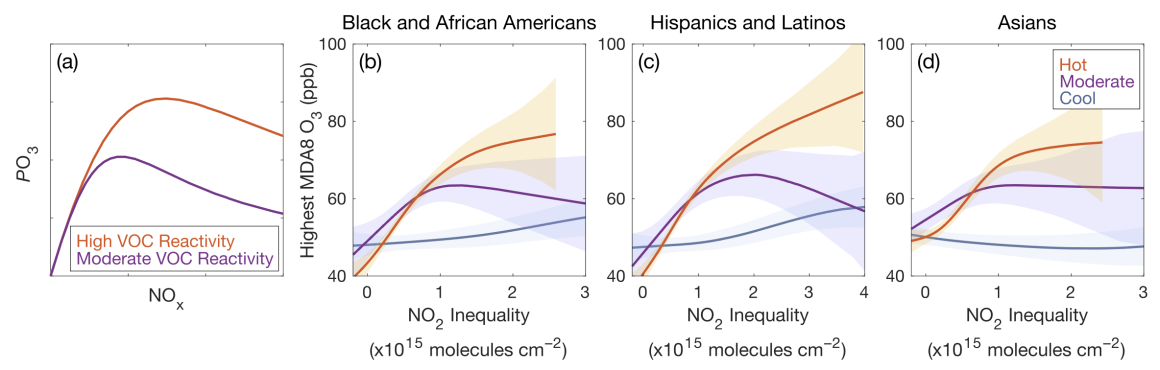
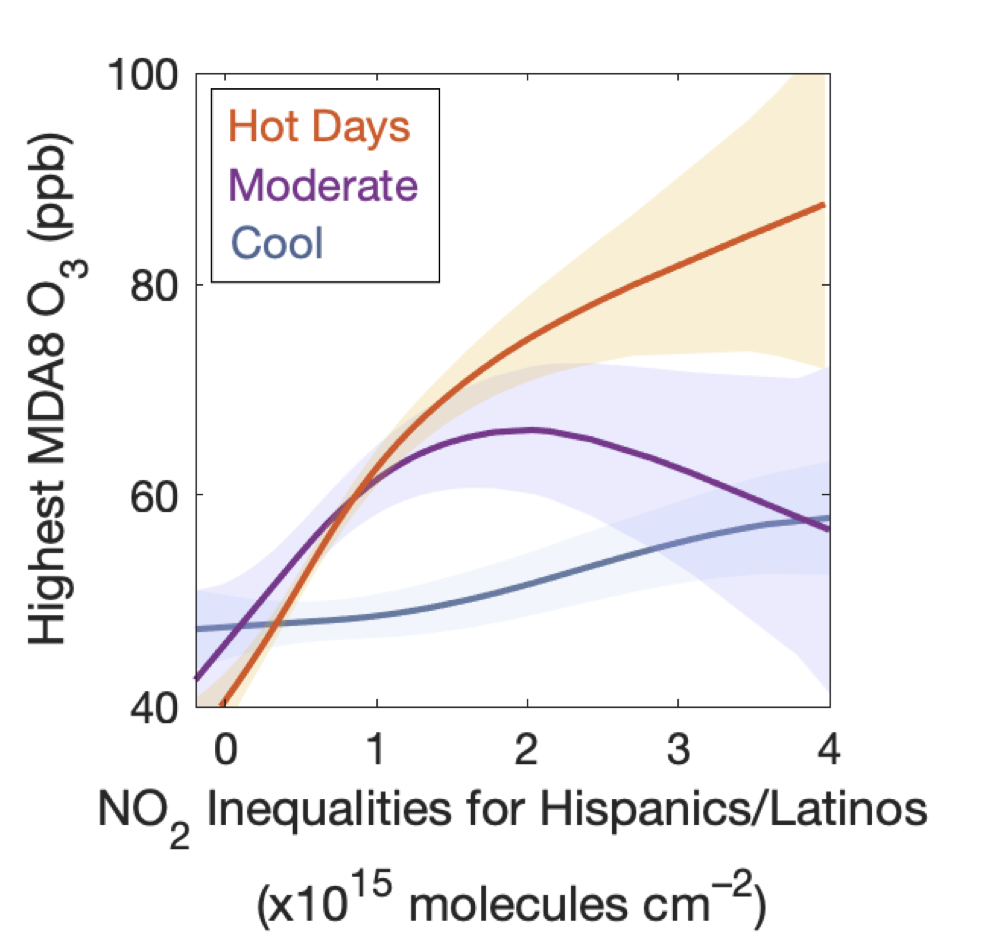
recent coverage of our work

We can see factory farm pollution all the way from space. But communities of color face the worst ammonia pollution on the ground
Led by Akirah Epps and Isabella Dressel, we use satellite data to observe inequalities and evaluate policies around industrialized swine operations in North Carolina




